Full solution
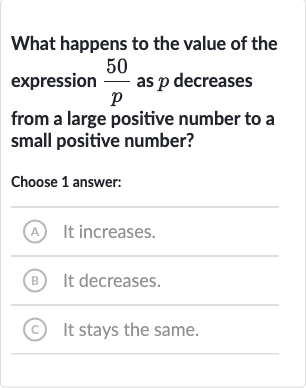
Q. What happens to the value of the expression as decreases from a large positive number to a small positive number?Choose answer:(A) It increases.(B) It decreases.(C) It stays the same.
- Understanding Inverse Proportion: Let's consider the expression . We want to understand how this expression changes as the value of changes. Since is in the denominator, we know that the value of the expression is inversely proportional to the value of . This means that as increases, the value of the expression decreases, and as decreases, the value of the expression increases.
- Illustrating with Examples: To illustrate this, let's take a large positive number for , say . The expression would then be . Now, if we decrease to a smaller positive number, say , the expression becomes . We can see that as decreased from to , the value of the expression increased from to .
- Generalizing Behavior: Since we are considering the behavior as decreases from a large positive number to a small positive number, we can generalize that the value of the expression increases as decreases, as long as remains positive.
More problems from Transformations of absolute value functions: translations and reflections
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help