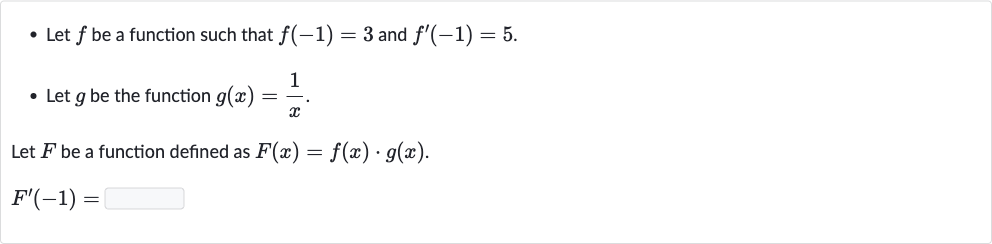Full solution
Q. - Let be a function such that and .- Let be the function .Let be a function defined as .
- Use Product Rule: To find , we need to use the product rule for differentiation, which states that if , then . We are given that and . We also know that , so we need to find .
- Find : First, let's find . The derivative of is . Now we can find by substituting with .
- Calculate : Calculate : .
- Apply Product Rule: Now we have all the necessary values to apply the product rule. We know , , and . Let's plug these values into the product rule formula.
- Substitute Values: Apply the product rule: .
- Find : Substitute the known values: .
- Complete Calculation: We need to find which is evaluated at . Since , .
- Complete Calculation: We need to find which is evaluated at . Since , .Now we can complete the calculation: .
More problems from Evaluate an exponential function
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help