AI tutor
Full solution
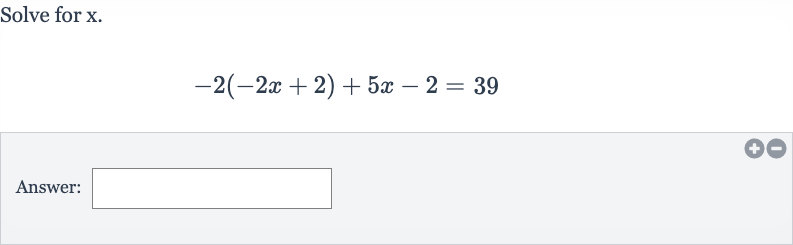
Q. Solve for .Answer:
- Distribute and Simplify: First, distribute the into the parentheses.
- Combine Like Terms: Combine like terms on the left side of the equation.
- Add and Isolate: Add to both sides to isolate the term with the variable .
- Divide and Solve: Divide both sides by to solve for .
More problems from Solve linear equations: mixed review
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help