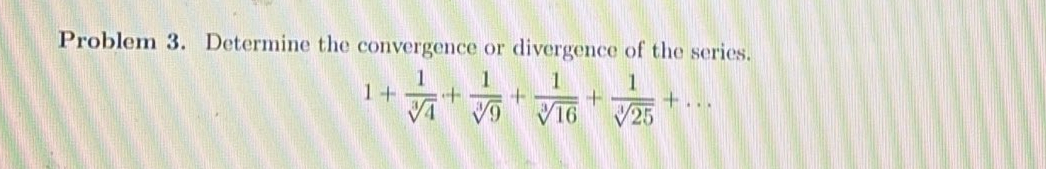Full solution
Q. Determine the convergence or divergence of the series.
- Identify series type: Step : Identify the series type.We're dealing with the series This looks like a p-series where each term is of the form .
- Compare with convergent series: Step : Compare to a known convergent series.For p-series, converges if p > 1. Here, (since the cube root of is ).
More problems from Multiplication with rational exponents
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help