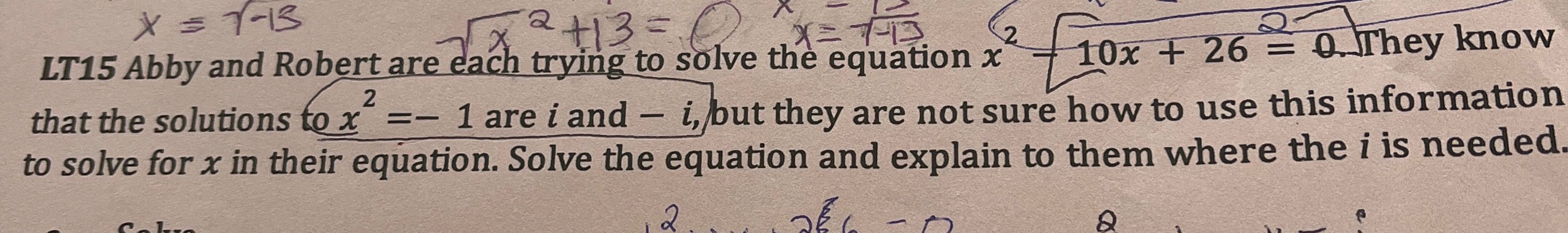AI tutor
Full solution
Q. LT Abby and Robert are each trying to solve the equation . They know that the solutions to are and , but they are not sure how to use this information to solve for in their equation. Solve the equation and explain to them where the is needed.
- Rewrite Equation: Step : Rewrite the equation to isolate the square root term.
- Square Both Sides: Step : Square both sides to eliminate the square root.
- Rearrange Polynomial: Step : Rearrange the equation to form a standard polynomial equation.
- Check Rational Roots: Step : Check for possible rational roots using the Rational Root Theorem.Possible rational roots could be factors of divided by factors of (leading coefficient).Possible roots: , , ,
- Test Possible Roots: Step : Test the possible roots in the polynomial.: (not a root): (not a root): (not a root): (not a root): (not a root): (not a root): (not a root): (not a root)
- Consider Complex Roots: Step : Since no rational roots are found, consider complex roots or use numerical methods or graphing to find roots.This step involves higher-level mathematics or graphing calculators, which might not be readily available.
More problems from Solve trigonometric equations
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
Question
. Find the value of in degrees.Write your answer in simplified, rationalized form. Do not round.____
Get tutor helpQuestionGet tutor help