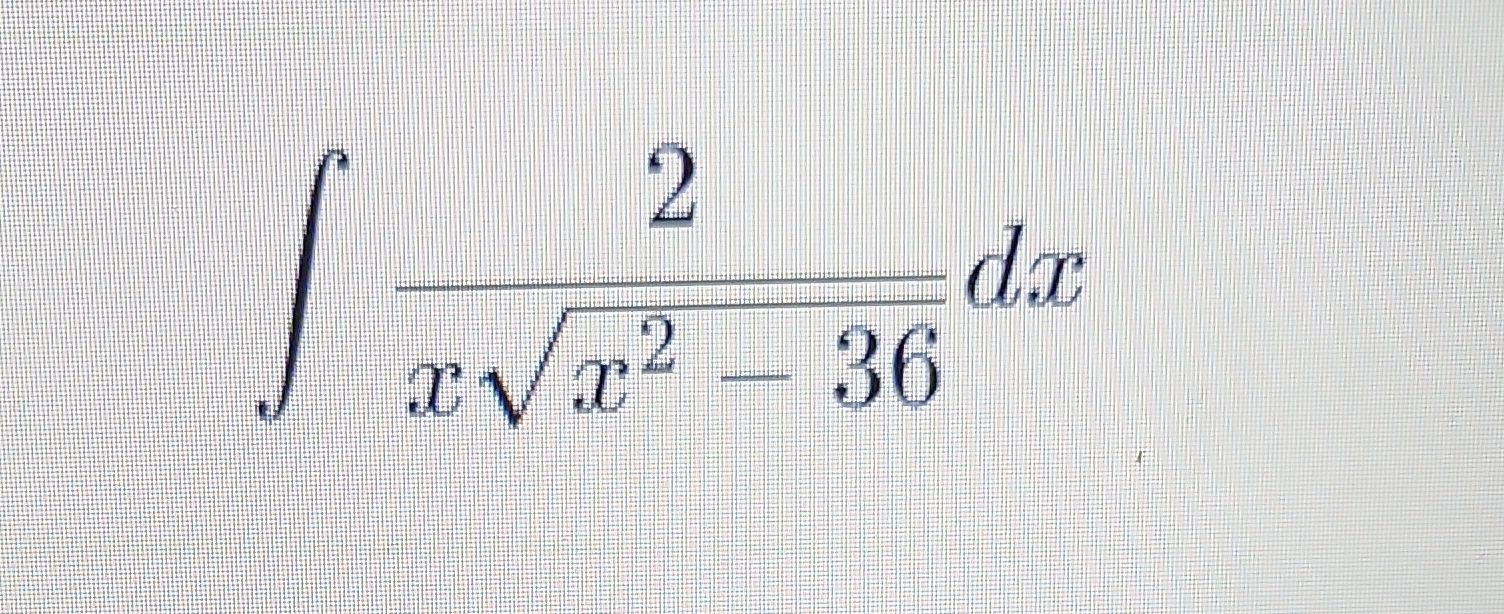AI tutor
Full solution
Q.
Evaluate the integral:
- Identify Integral: Let's identify the integral we need to solve:We can see that this integral suggests a trigonometric substitution because of the form under the square root. We will use the substitution , where in this case, because .
- Substitute : Substitute into the integral. Then, and . The integral becomes:
- Simplify Integral: Simplify the integral by canceling terms and using the identity . Since we are dealing with x > 6 (because of the original square root), \sec(\theta) > 0, and thus \tan(\theta) > 0, we can remove the absolute value:
- Integrate with Integrate with respect to , where is the constant of integration.
- Substitute back for : We need to substitute back for using our original substitution . We have , and to find , we use the definition of secant: , so . Then .