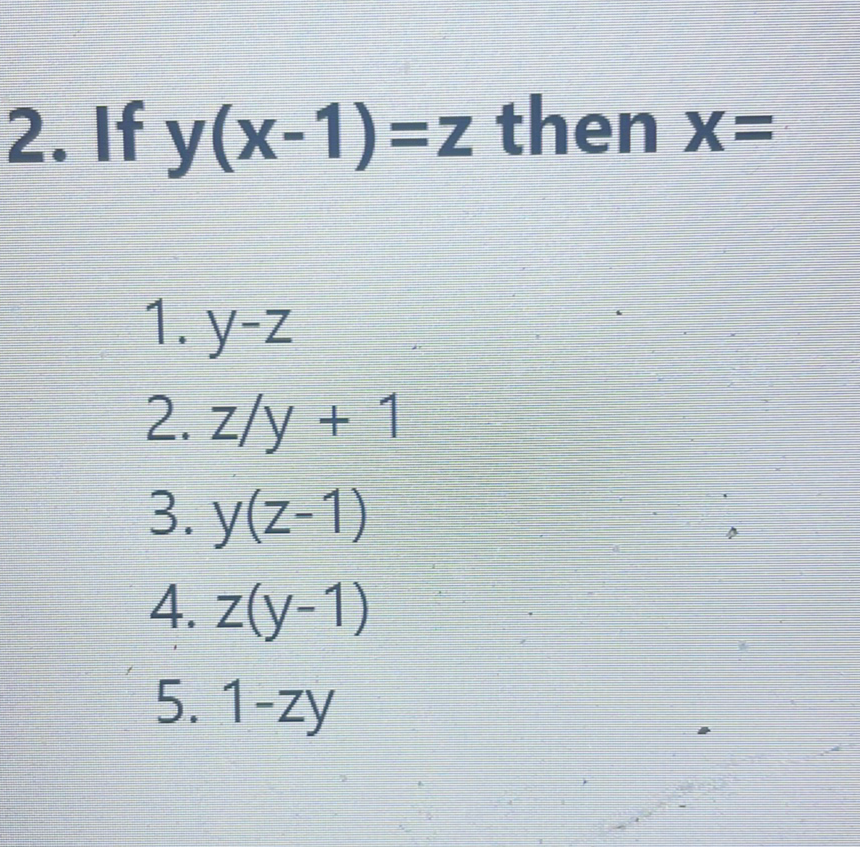AI tutor
Full solution
Q. . If then . . . . . -
- Isolate x term: Given the equation , we want to solve for in terms of and . First, we isolate the term with by dividing both sides of the equation by :
- Add to both sides: Next, we add to both sides of the equation to solve for :
- Check for matching option: Now we have the expression for in terms of and . We can check the given options to see which one matches our derived expression:The correct option that matches this expression is .
More problems from Euler's method
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help