Full solution
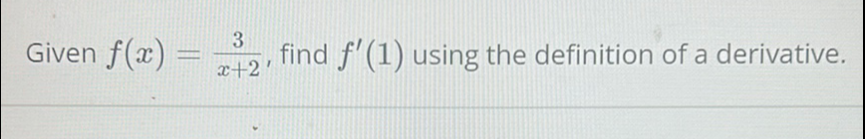
Q. Given , find using the definition of a derivative.
- Given Function: We are given the function and we need to find its derivative at using the definition of a derivative. The definition of a derivative is:Let's apply this definition to our function.
- Substitute : First, we need to find the expression for . This means we will substitute for in the function :
- Plug into Derivative Definition: Now, we will plug and into the definition of the derivative:
- Find Common Denominator: Next, we need to find a common denominator for the terms in the numerator to combine them:The common denominator is , so we rewrite the numerator:
- Simplify Numerator: Now, we simplify the numerator:So the expression becomes:
- Cancel out h: We can now cancel out the h in the numerator and denominator:
- Take the Limit: Now we can take the limit as approaches :
- Substitute : Finally, we substitute into the derivative to find :
More problems from Evaluate expression when two complex numbers are given
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help