AI tutor
Welcome to Bytelearn!
Let’s check out your problem:
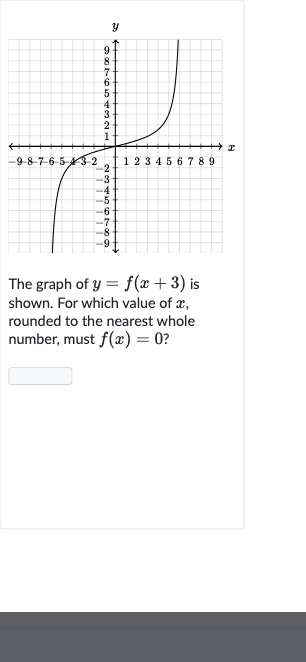
The graph of is shown. For which value of , rounded to the nearest whole number, must ?
Full solution
Q. The graph of is shown. For which value of , rounded to the nearest whole number, must ?
- Understand Transformation: To solve for the value of where , we need to understand the transformation applied to the function to get the graph of .The graph of is a horizontal shift of the graph of to the left by units.This means that the -values on the graph of are units less than the corresponding -values on the graph of .
- Find value of for : To find when , we need to find what value of results in .Since , it implies that , because when you input , you get .Hence, the value of is , when .
