Full solution
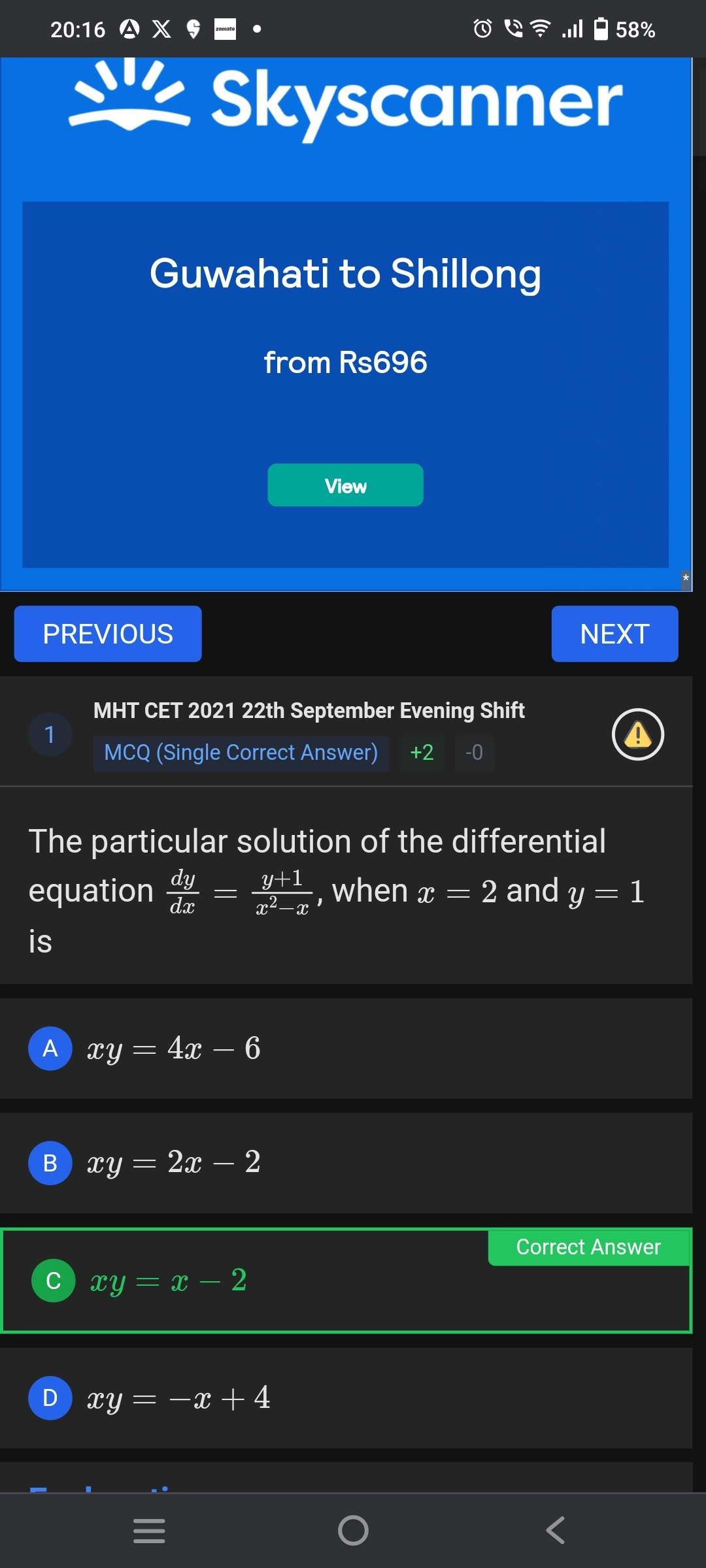
Q. The particular solution of the differential equation , when and isA) B) C) D)
- Given Differential Equation: Given the differential equation and the initial condition , . We need to find the particular solution that fits this condition.
- Simplify Equation: Simplify the differential equation by factoring the denominator: .
- Apply Initial Condition: Use the initial condition to plug in and into the equation: . This confirms that the slope at , is .
- Integrate Differential Equation: To find the particular solution, we need to integrate the differential equation. We can separate variables and integrate: .
- Exponentiate to Solve for y: Integrate both sides: , where is the integration constant.
- Find Integration Constant: Exponentiate both sides to solve for : .
- Substitute for Particular Solution: Use the initial condition to find : , so .
- Finalize Solution: Substitute back into the equation: . Solve for : .
- Rewrite in Terms of x: Rewrite in terms of to match the answer choices: . Multiply both sides by : .
- Simplify the Expression: Simplify the expression: . This simplifies to .
More problems from Euler's method
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help